Varicella-Zoster Virus (VZV)
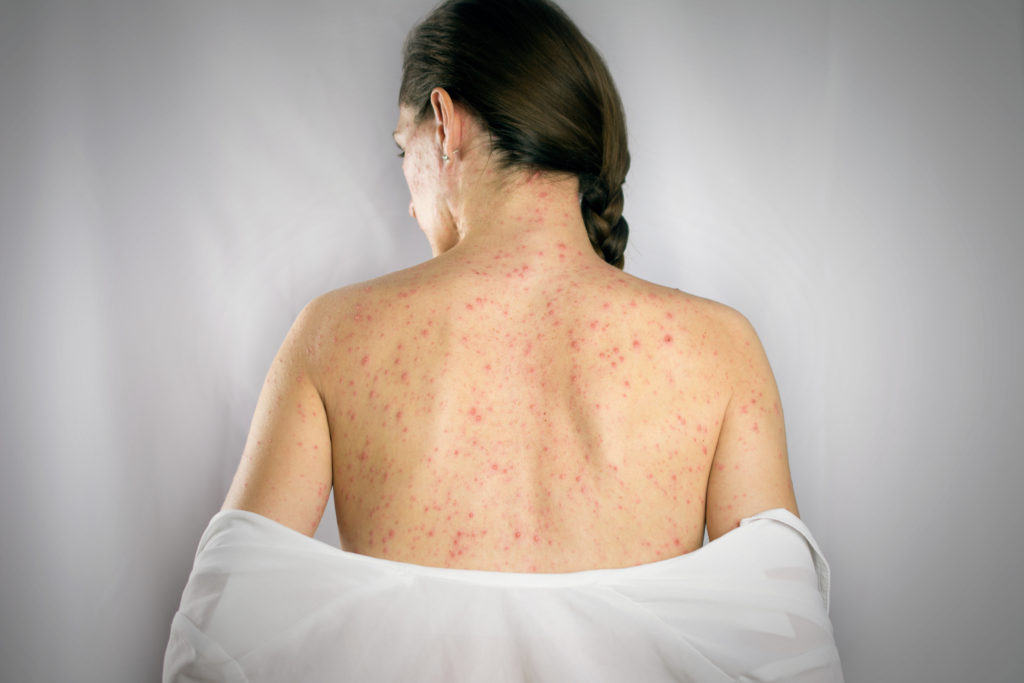
Varicella, more commonly known as the chickenpox, is a highly communicable infection caused by a virus. Adults can contract chickenpox, but mainly children fall victim to this nasty, but not dangerous virus. The first sign of chickenpox is when a person gets extremely itchy and develops a skin rash with red blisters. Eventually the red blisters will start to pop and puss. The blisters will go through a healing process, which includes scabbing over before going away. A person is considered to be a higher risk of chickenpox if:
- They have not had the chickenpox previously
- They have not been vaccinated for it
- They work in a school or with children
- They have young children who can be exposed to it
How do you know if you have chicken pox?
Symptoms appear within ten to twenty-one days after the infected person has been in contact with the virus. Most individuals with chickenpox recover in about 2 weeks. Chickenpox is commonly mild in children, but in severe cases, the blisters can spread to your nose, mouth, eyes, and even genitals, which can be very painful. Adults have a harder time recovering from this virus. Symptoms of the chickenpox are most commonly blistering, body aches, fever, fatigue, irritability, loss of appetite, and headaches.
How do you contract the chickenpox?
It is very easy to get the chickenpox, especially for kids! You can contract the virus by breathing in particles that come from chickenpox blisters or by touching something that has been infected.
Chickenpox is most contagious in the early days before the symptoms even appear, all the way until all the blisters are dried and crusted.
The best way to prevent the spread of the virus is to get the vaccine. Children who have never had chickenpox should get two rounds of the injection as an infant and as they enter kindergarten. Adults can consult with their primary care doctor if they are concerned about getting vaccinated.
Is there a major risk for the chickenpox?
Adults are considered to be a higher risk for developing complications from chickenpox. Children generally do not face high risks; however, it is not impossible. Those with weakened immune systems can also be at a higher risk.
The verdict
Chickenpox is very common for children and less common for adults, but nonetheless it is not anything to worry about. As always, Dr. Dharia and his team at Palm Beach Internal Medicine are here to help.
